
Clinical Report: Predictive Infection Surveillance in a 1,200-Bed National Military Hospital
Clinical Report: Predictive Infection Surveillance in a 1,200-Bed National Military Hospital
Clinical Report: Predictive Infection Surveillance in a 1,200-Bed National Military Hospital
Clinical Report: Predictive Infection Surveillance in a 1,200-Bed National Military Hospital
Published 10/04/2025
Published 10/04/2025
Published 10/04/2025

Dr. Vasikasin
Dr. Vasikasin
Dr. Vasikasin
Highlights
A recent clinical study has demonstrated that the NEX Intelligence platform achieves state-of-the-art performance in real-time infection surveillance and early prediction of multidrug-resistant organisms — with an AUC-ROC of 0.89 and 87% sensitivity for predicting CRE acquisition up to seven days in advance.
Background
The infection prevention and control (IPC) team at Phramongkutklao Hospital, a 1,200-bed military hospital in Thailand, has historically relied on an entirely manual surveillance system. This system required retrospective reviews to identify and collate hospital-acquired infections, making the early identification of infection transmission patterns and rapid response incredibly challenging.
Deployment
In January 2025, the hospital partnered with NEX to deploy an AI-driven infection surveillance system. The project focused on building real-time pipelines for the detection and monitoring of key healthcare-associated infections, including Multi-Drug-Resistant Organisms (MDROs), Bloodstream Infections (BSIs), and Device-associated infections (DAIs). The deployment was integrated directly with live microbiology feeds and electronic patient records, creating a centralised, automated platform for IPC teams to track, manage, and prevent infections.
Highlights
A recent clinical study has demonstrated that the NEX Intelligence platform achieves state-of-the-art performance in real-time infection surveillance and early prediction of multidrug-resistant organisms — with an AUC-ROC of 0.89 and 87% sensitivity for predicting CRE acquisition up to seven days in advance.
Background
The infection prevention and control (IPC) team at Phramongkutklao Hospital, a 1,200-bed military hospital in Thailand, has historically relied on an entirely manual surveillance system. This system required retrospective reviews to identify and collate hospital-acquired infections, making the early identification of infection transmission patterns and rapid response incredibly challenging.
Deployment
In January 2025, the hospital partnered with NEX to deploy an AI-driven infection surveillance system. The project focused on building real-time pipelines for the detection and monitoring of key healthcare-associated infections, including Multi-Drug-Resistant Organisms (MDROs), Bloodstream Infections (BSIs), and Device-associated infections (DAIs). The deployment was integrated directly with live microbiology feeds and electronic patient records, creating a centralised, automated platform for IPC teams to track, manage, and prevent infections.
Highlights
A recent clinical study has demonstrated that the NEX Intelligence platform achieves state-of-the-art performance in real-time infection surveillance and early prediction of multidrug-resistant organisms — with an AUC-ROC of 0.89 and 87% sensitivity for predicting CRE acquisition up to seven days in advance.
Background
The infection prevention and control (IPC) team at Phramongkutklao Hospital, a 1,200-bed military hospital in Thailand, has historically relied on an entirely manual surveillance system. This system required retrospective reviews to identify and collate hospital-acquired infections, making the early identification of infection transmission patterns and rapid response incredibly challenging.
Deployment
In January 2025, the hospital partnered with NEX to deploy an AI-driven infection surveillance system. The project focused on building real-time pipelines for the detection and monitoring of key healthcare-associated infections, including Multi-Drug-Resistant Organisms (MDROs), Bloodstream Infections (BSIs), and Device-associated infections (DAIs). The deployment was integrated directly with live microbiology feeds and electronic patient records, creating a centralised, automated platform for IPC teams to track, manage, and prevent infections.
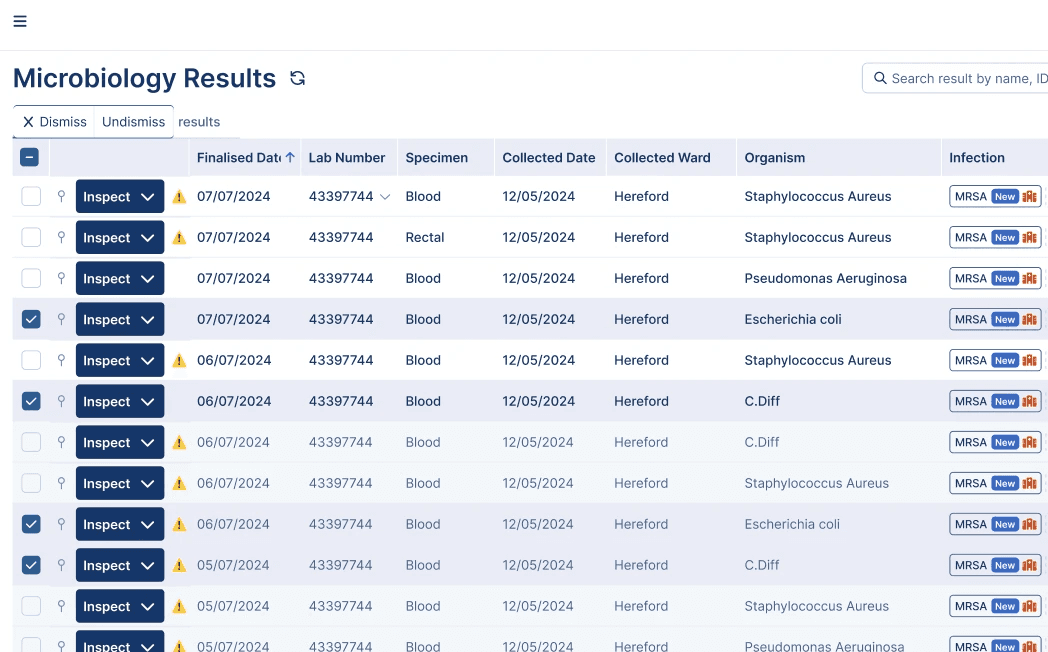
Results feed tracking and tagging new microbiological records with MDRO, BSI, and DAI labels for review and surveillance from the NEX Infection Centre.Selective screening consistently outperforms universal screening and no intervention, especially in lower-prevalence settings.¹
Results feed tracking and tagging new microbiological records with MDRO, BSI and DAI labels for review and surveillance from the NEX Infection Centre. Selective screening consistently outperforms universal screening and no intervention, especially in lower-prevalence settings.¹
Results feed tracking and tagging new microbiological records with MDRO, BSI, and DAI labels for review and surveillance from the NEX Infection Centre.Selective screening consistently outperforms universal screening and no intervention, especially in lower-prevalence settings.¹
Results feed tracking and tagging new microbiological records with MDRO, BSI, and DAI labels for review and surveillance from the NEX Infection Centre.Selective screening consistently outperforms universal screening and no intervention, especially in lower-prevalence settings.¹
Early Results from Hospital Deployment
The NEX system demonstrated rapid impact within weeks of implementation—digitising infection records, enabling real-time data visibility, streamlining workflows, and receiving strong frontline feedback.
Early Results from Hospital Deployment
The NEX system demonstrated rapid impact within weeks of implementation—digitising infection records, enabling real-time data visibility, streamlining workflows and receiving strong frontline feedback.
Early Results from Hospital Deployment
The NEX system demonstrated rapid impact within weeks of implementation—digitising infection records, enabling real-time data visibility, streamlining workflows, and receiving strong frontline feedback.
Early Results from Hospital Deployment
The NEX system demonstrated rapid impact within weeks of implementation—digitising infection records, enabling real-time data visibility, streamlining workflows, and receiving strong frontline feedback.
Full Digital Centralisation
Within three weeks, full digital centralisation of infection records, searchable by patient, location, and organism, was achievable.
Within three weeks, full digital centralisation of infection records, searchable by patient, location and organism, was achievable.
Real-time Awareness
Live data feeds showed real-time active cases of infection by ward across the hospital, indicating when institution-defined thresholds were exceeded.
Streamlined Surveillance
The system significantly reduced the administrative burden from manual data entry and spreadsheet tracking.
Positive Staff Feedback
Positive staff feedback on usability and interface clarity, including user and site-specific customisability.

"We finally have real-time visibility across the entire hospital. It has dramatically reduced time-consuming tasks and is already helping us prioritise more effectively and prepare faster."
— Dr. Vasin Vasikasin, Assistant Professor and Consultant in Infectious Diseases at Phramongkutklao Hospital, Honorary Research Fellow at Imperial College London
Predicting Infection Acquisition for Targeted Prevention
Predicting Infection Acquisition for Targeted Prevention
Predicting Infection Acquisition
for Targeted Prevention
We are in the process of validating our early warning models, designed to predict the acquisition of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) — one of the most clinically significant multidrug-resistant organisms in hospital settings (Center for Disease Control and Prevention).
The system generates live daily risk scores for all inpatients, identifying those at highest risk of acquiring CRE before a positive microbiological result is confirmed. These scores are calculated using live data feeds, drawing on a range of patient-specific variables, including microbiology history, antimicrobial usage, device exposure, and ward movements.
NEX Infection Intelligence identifies high-risk contacts exposed to a source CRE case, with predicted risk of testing positive.
We are in the process of validating our early warning models, designed to predict the acquisition of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) — one of the most clinically significant multidrug-resistant organisms in hospital settings (Center for Disease Control and Prevention).
The system generates live daily risk scores for all inpatients, identifying those at highest risk of acquiring CRE before a positive microbiological result is confirmed. These scores are calculated using live data feeds, drawing on a range of patient-specific variables, including microbiology history, antimicrobial usage, device exposure, and ward movements.
NEX Infection Intelligence identifies high-risk contacts exposed to a source CRE case, with predicted risk of testing positive.
We are in the process of validating our early warning models, designed to predict the acquisition of Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales (CRE) — one of the most clinically significant multidrug-resistant organisms in hospital settings (Center for Disease Control and Prevention).
The system generates live daily risk scores for all inpatients, identifying those at highest risk of acquiring CRE before a positive microbiological result is confirmed. These scores are calculated using live data feeds, drawing on a range of patient-specific variables, including microbiology history, antimicrobial usage, device exposure, and ward movements.
NEX Infection Intelligence identifies high-risk contacts exposed to a source CRE case, with predicted risk of testing positive.
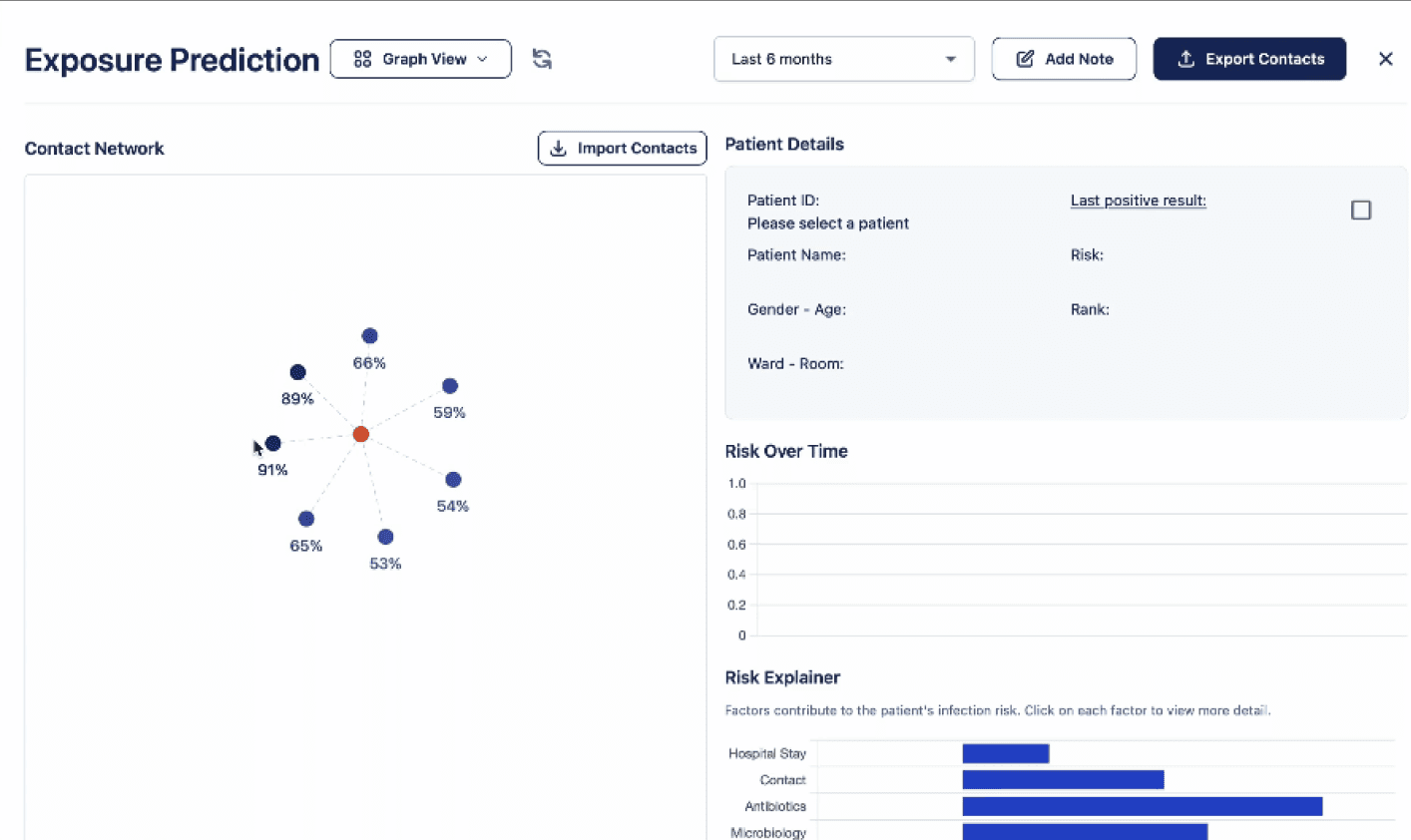




Early validation results over six months of prospectively generated data suggest strong predictive performance, with an AUC-ROC of 0.89, sustained across a prospective dataset including both clinical and screening cultures². The model enables risk stratification up to seven days before confirmed acquisition.
Early validation results over six months of prospectively generated data suggest strong predictive performance, with an AUC-ROC of 0.89, sustained across a prospective dataset including both clinical and screening cultures². The model enables risk stratification up to seven days before confirmed acquisition.
Early validation results over six months of prospectively generated data suggest strong predictive performance, with an AUC-ROC of 0.89, sustained across a prospective dataset including both clinical and screening cultures². The model enables risk stratification up to seven days before confirmed acquisition.
0.89 AUC-ROC
Performance in predicting colonisation with CRE among clinical and screening cultures.
7-days ahead
In net savings from genomically guided interventions in early transmission to a US-based hospital
USD$290M
High sensitivity in the prediction of positive versus negative results.
0.89 AUC-ROC
0.89 AUC-ROC
Performance in predicting colonisation with CRE among clinical and screening cultures.
Performance in predicting colonisation with CRE among clinical and screening cultures.
7-days ahead
7-days ahead
In net savings from genomically guided interventions in early transmission to a US-based hospital
In net savings from genomically guided interventions in early transmission to a US-based hospital
87% sensitivity
87% sensitivity
High sensitivity in the prediction of positive versus negative results.
High sensitivity in the prediction of positive versus negative results.
Conclusion
Conclusions
This collaboration represents the growing transition from retrospective audits and IPC surveillance to real-time, data-driven, more anticipatory infection control. The project has demonstrated the feasibility and utility of automated surveillance in a large, high-volume hospital environment with electronic health records — streamlining IPC workflows, improving situational awareness and laying the foundations for predictive infection prevention.
NEX continues working closely with frontline IPC teams to ensure the system delivers actionable intelligence — where and when it’s needed most!
This collaboration represents the growing transition from retrospective audits and IPC surveillance to real-time, data-driven, more anticipatory infection control. The project has demonstrated the feasibility and utility of automated surveillance in a large, high-volume hospital environment with electronic health records — streamlining IPC workflows, improving situational awareness, and laying the foundations for predictive infection prevention.
NEX continues working closely with frontline IPC teams to ensure the system delivers actionable intelligence — where and when it’s needed most!
Conclusions
This collaboration represents the growing transition from retrospective audits and IPC surveillance to real-time, data-driven, more anticipatory infection control. The project has demonstrated the feasibility and utility of automated surveillance in a large, high-volume hospital environment with electronic health records — streamlining IPC workflows, improving situational awareness and laying the foundations for predictive infection prevention.
NEX continues working closely with frontline IPC teams to ensure the system delivers actionable intelligence — where and when it’s needed most!
References
References
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About CRE: Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. 3 Aug. 2023, https://www.cdc.gov/cre/about/index.html. Accessed 10 Apr. 2025.
Vasikasin, D. Prospective Evaluation of a Machine Learning-Based Real-Time Multidrug-Resistant Organism Prediction System. Featured talk, ESCMID Global Conference 2025, 13 Apr. 2025, Vienna, Austria.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About CRE: Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. 3 Aug. 2023, https://www.cdc.gov/cre/about/index.html. Accessed 10 Apr. 2025.
Vasikasin, D. Prospective Evaluation of a Machine Learning-Based Real-Time Multidrug-Resistant Organism Prediction System. Featured talk, ESCMID Global Conference 2025, 13 Apr. 2025, Vienna, Austria.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About CRE: Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales. 3 Aug. 2023, https://www.cdc.gov/cre/about/index.html. Accessed 10 Apr. 2025.
Vasikasin, D. Prospective Evaluation of a Machine Learning-Based Real-Time Multidrug-Resistant Organism Prediction System. Featured talk, ESCMID Global Conference 2025, 13 Apr. 2025, Vienna, Austria.
Get Started Today
Join hospitals and health systems already using NEX to stay ahead of infection threats.
Get Started Today
Join hospitals and health systems already using NEX to stay ahead of infection threats.
Get Started Today
Join hospitals and health systems already using NEX to stay ahead of infection threats.
Get Started Today
Join hospitals and health systems already using NEX to stay ahead of infection threats.




